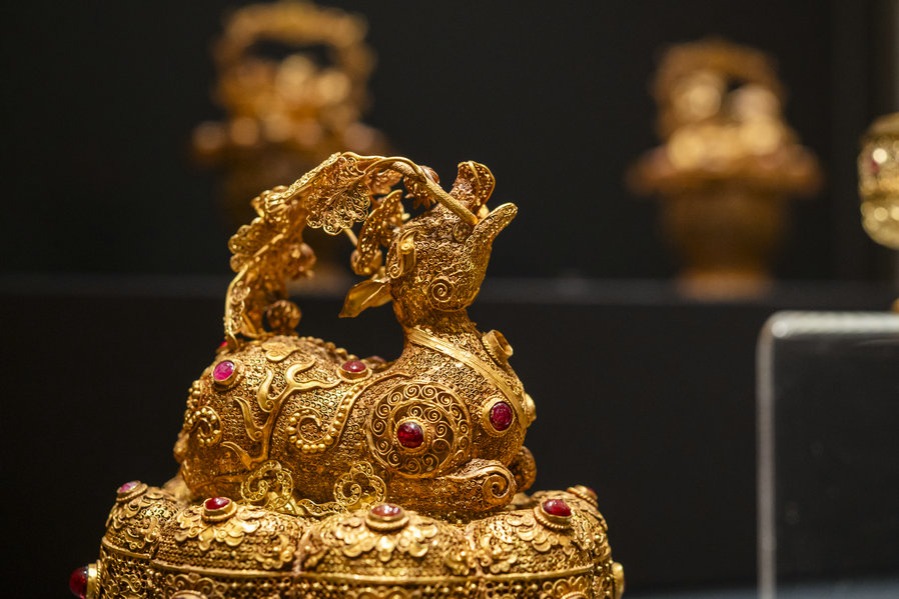
Museum shows its true colors
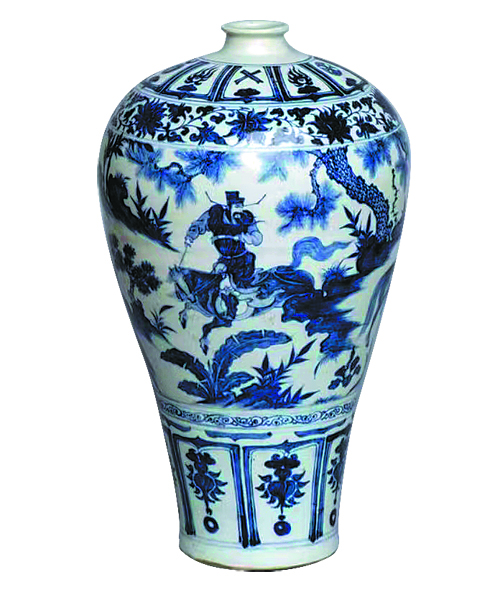


Stories of precious stones
To design such a comprehensive exhibition, it is natural to first credit jade when reviewing the lasting legacies of cyan in Chinese culture.
From arc-shaped huang or disc-like bi of the Neolithic period (10,000 to 4,000 years ago), the 3,000-odd-year ritual cong, a straight tube with a circular bore and square outer, to exquisite decorations from the Warring States Period (475-221 BC), jade demonstrated people's understanding of the color in early history, but was not based solely on aesthetics.
"Jade artifacts served as key symbols in ceremonies and sacrificial rituals," Tan Ping, director of Art Exhibitions China, says. "The exhibits are witnesses to the unified ceremonial system of a centralized authority, reflecting the unity of Chinese civilization."
Once seen as a crucial indicator of national governance, jade later played a key role in aristocratic burial customs during the Han Dynasty (206 BC-AD 220) as a bridge to connect with the afterworld.
Following the 3rd century, jade was widely worn as a daily accessory by various social classes in China.
"Ancient Chinese referred to jade items to worship heaven," Zhang Lei explains.
"They also often used this cultural icon to describe men with virtue.
"From the very beginning of our civilization, jade has been seen as something precious," she continues. "People tend to have some special affection for its color, its soft green revealing elegance. The color also represents everything growing in nature."
Compared with this dominating role of jade, the significance of turquoise in ancient China seems to have been overshadowed. However, like many other key hubs of ancient civilizations, China also had a long tradition to admire such a precious stone, as the exhibition shows.
A bronze handle inlaid with turquoise from the Western Zhou Dynasty (c.11th century-771 BC) is such an example.
Back then, turquoise was often used as decorations on bronze weapons, ceremonial items, or settings on horses and chariots. An exhibited necklace of turquoise from the same period also reveals Chinese people's admiration for cyan.