China builds satellite constellations to enable smart connectivity from space
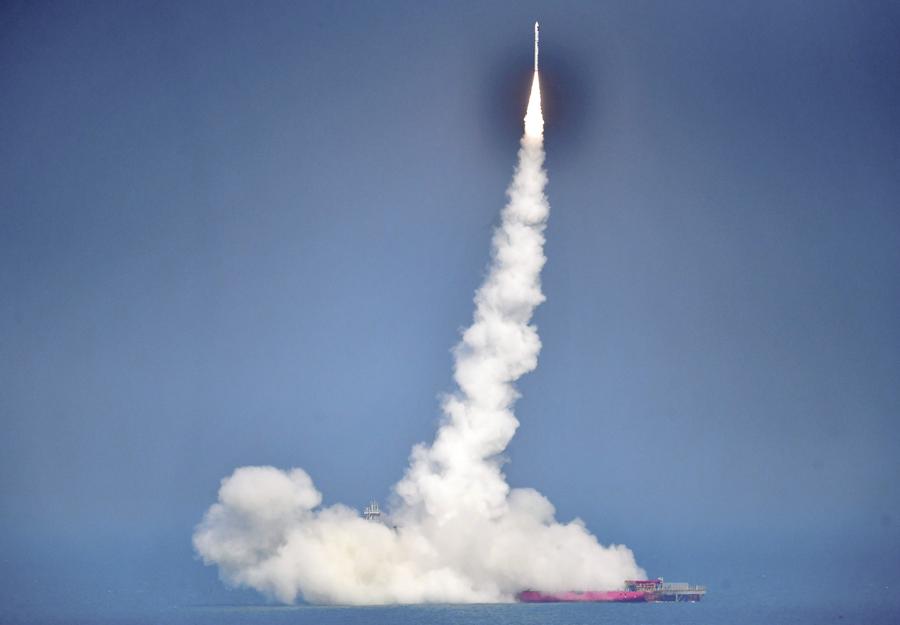


BEIJING -- With four new satellites launched this month to expand the Tianqi constellation, China is accelerating a presence in low-Earth orbit to support its surging demand for smart device connectivity.
Following SpaceX's lead, an increasing number of Chinese aerospace firms have begun constructing Starlink-style satellite networks over the past years. Some of these commercial space firms are specifically targeting the development of critical digital infrastructure for IoT (Internet of Things) connectivity.
Tianqi, a satellite constellation developed and operated by GuoDianGaoKe Technology, has now reached its first phase with 37 satellites in orbit, forming a global network that provides services for smart cities, marine monitoring, emergency communications and environmental monitoring.
Upon the deployment of these four satellites, the constellation's revisit time will be shortened to just five minutes, representing a 37.5 percent enhancement in its operational efficiency, which is vital for facilitating real-time data transmission.
"Tianqi has filled a technological gap in China's low-orbit IoT satellite field. Its technical systems, performance and terminal indicators have reached internationally leading levels," said Lyu Qiang, chairman of the Beijing-based firm.
Tianqi is now exploring the expansion into consumer markets, including smartphones, smart vehicles and wearable devices. The company plans to design and launch additional satellites in its second phase, aimed at enhancing consumer-level applications.
CAR CONNECTIVITY
Another commercial satellite constellation project, funded by a leading Chinese automaker, is set to revolutionize intelligent connectivity for road vehicles from space.
Geely's Future Mobility Constellation, developed by commercial space subsidiary Geespace, has placed 30 satellites across three orbital planes. The constellation expanded last September with the launch of an additional 10 satellites.
This deployment enables 90 percent global coverage, making it the first Chinese commercial space enterprise to offer low-orbit satellite communication services to international users.
The constellation is focusing on scenarios in intelligent driving, smart mobility and consumer electronics, said Wang Yang, founder and CEO of Geespace.
It has a three-phase plan: 72 satellites for global real-time data communication in Phase One, 264 satellites for direct smartphone connectivity in Phase Two, and 5,676 satellites for global broadband services in Phase Three, according to Wang.
Supported by the constellation, some Geely's Zeekr and Galaxy electric vehicles now feature space communication. Users can send and receive messages via satellite when ground networks are disrupted.
In June last year, Geely's satellite constellation initiated international commercial operations in parts of the Middle East, and it plans to extend services to North Africa by 2025. This expansion marked a milestone for Chinese commercial space firms on the international stage.
Industry analysts note that satellite networks are particularly valuable for autonomous driving applications, as they provide reliable connectivity in areas where traditional networks are unavailable.
According to Grand View Research, the global autonomous driving market is projected to reach $557 billion by 2030. The Chinese satellite constellation is positioning itself to capture a significant market share by partnering with multiple car manufacturers.
Geespace has established a state-of-the-art factory in Taizhou, a city in eastern China, leveraging modular design and intelligent manufacturing technologies. This facility is engineered to cut production costs by 45 percent and can produce 1 to 2 satellites per day, with an annual capacity of up to 500 satellites.
Another rapidly growing economic sector in China is also creating huge opportunities for low-Earth orbit satellite internet, as the increasing number of drones relies on low-altitude intelligent networking.
China is accelerating the development of low-altitude intelligent networking infrastructure and advancing the research and construction of 5G/5G-A, Beidou navigation, and satellite internet technologies.
"Low-altitude intelligent networking, as the digital foundation for the low-altitude economy, can ensure the safe operation of low-altitude aircraft," said Lu Feng, a researcher from a Beijing technology research institute.