China's coral spawning breakthrough offers fresh hope for threatened reefs


NANNING -- A team of marine scientists from Guangxi University has achieved a remarkable breakthrough in coral conservation just ahead of World Oceans Day, which is observed on Sunday.
Off the coast of Weizhou Island, located at 21 degrees north latitude in South China's Guangxi Zhuang autonomous region, the team has mastered a key technology to trigger large-scale coral spawning in high-latitude regions.
This milestone enables controlled sexual reproduction of corals, marking a vital step toward transforming Weizhou Island into a sanctuary for corals threatened by global climate change.
"This is a game-changer," said Huang Wen, associate professor at the School of Marine Sciences at Guangxi University. "After 11 years of research, we've moved from simply planting corals to breeding them, helping to create thriving underwater ecosystems."
Coral reefs, often referred to as the "tropical rainforests of the ocean," occupy just 0.2 percent of the seafloor but support over a quarter of all marine species. However, global warming and human activities have led to widespread coral bleaching.
Weizhou Island had not been exempt from this decline; coral cover there plunged from 60 percent in the 1980s to less than 5 percent by 2015.
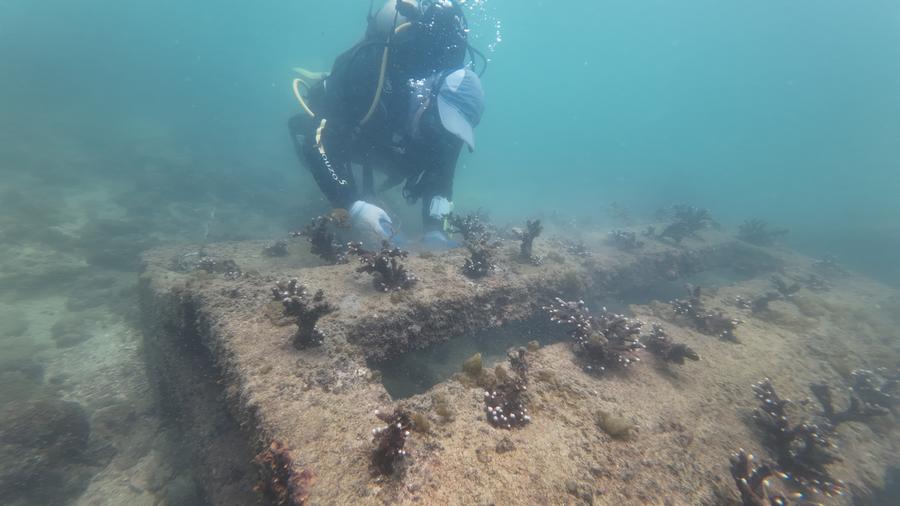
In 2015, the Guangxi University team embarked on an arduous journey to restore coral reefs. They cultivated coral colonies in laboratories, salvaged fragments from the seafloor, and anchored them to seed trays before divers carefully placed them on the seabed.
Their 2,000-square-meter restoration zone has seen remarkable progress, with coral cover quadrupling to 20 percent over three years. To date, the team has installed 1,520 artificial reefs, transplanted over 80,000 coral colonies, and restored 30 hectares of reefs.
However, planting corals is just the beginning. "For restoration to truly succeed, corals must reproduce naturally," said Gong Sanqiang, another associate professor at the School of Marine Sciences. "Sexual reproduction not only boosts genetic diversity but also strengthens resilience to environmental changes."
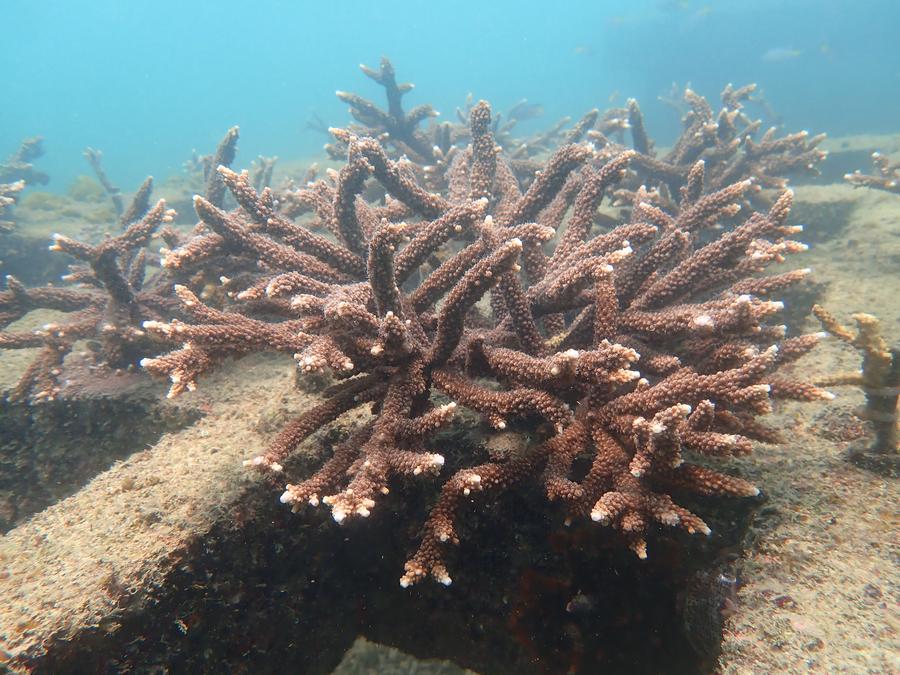

Coral spawning is brief, usually lasting just hours each year. To capture this moment, the team developed techniques to identify spawning windows by monitoring the corals' gonadal development alongside seawater conditions.
Their efforts paid off in mid-May, when the researchers pinpointed a 72-hour "golden window" for coral spawning off Weizhou Island.
Underwater, divers captured stunning images of corals releasing large clusters of pink reproductive bundles. Meanwhile, some other scientists from the team activated the water flow control system and used specialized methods to induce spawning, collecting significant numbers of eggs and sperm. In the laboratory, researchers worked around the clock to separate the gametes and preserve them in liquid nitrogen.
According to Gong, this expedition confirmed that the restored corals had reached sexual maturity and are capable of mass reproduction to repopulate surrounding areas.
In their laboratory, each liquid nitrogen tank now stores reproductive cells from various coral populations.
"These liquid nitrogen tanks are a 'Noah's Ark' for corals," said Yu Kefu, team leader and dean of the School of Marine Sciences. "They hold the key to future restoration efforts."
- China's coral spawning breakthrough offers fresh hope for threatened reefs
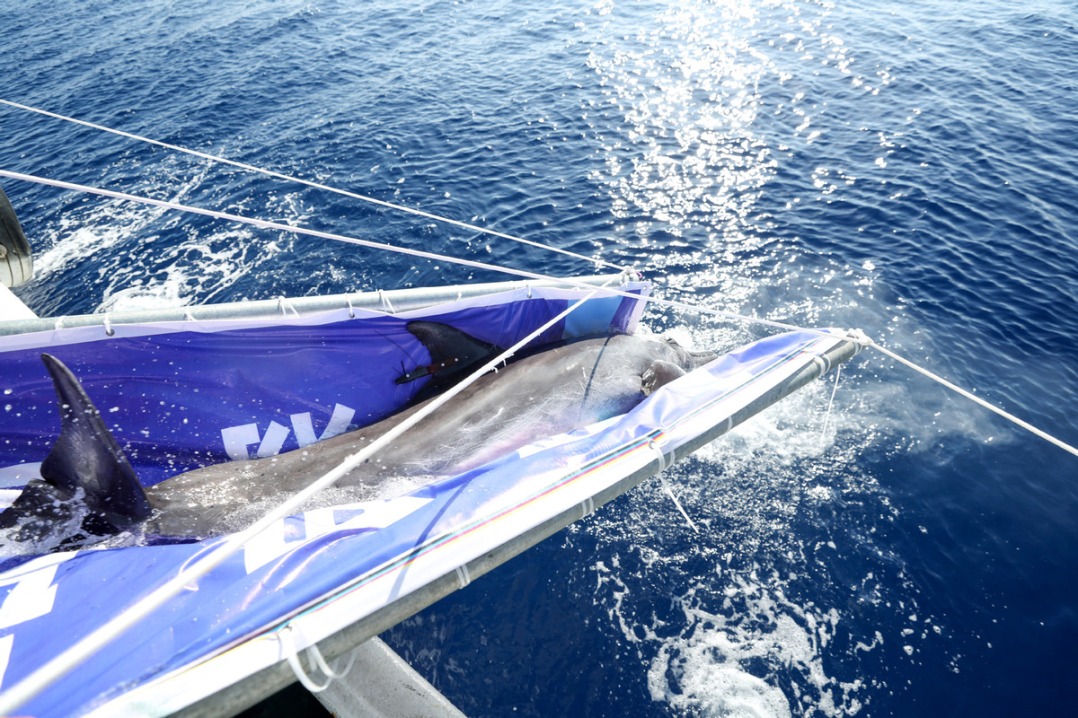
- Stranded dolphin returns to sea after receiving specialized care
- Report seeks unity for global ocean governance
- Reformed gaokao offered in 29 provincial-level regions
- Well-wishers help math scholar's video go viral
- AI helps keep candidates safe, honest